This article will introduce the laser welding equipment selection and configuration of the hands-on part, will be divided into eight chapters to further introduce the laser welding welding process, equipment components, software methods, quality issues and defect prevention guidelines. And interspersed with other knowledge of laser welding, is committed to creating a more comprehensive and close to the industrial production of popular science articles.

1. Welding process and principle
1.1 Definition of welding
Welding is a process in which two or more materials of the same or different species are joined together by atomic or intermolecular bonding and diffusion. Promote the combination and diffusion between atoms and molecules is the method of heating or pressurization, or both heating and pressurization.
1.2 Classification of metal welding
Metal welding is classified according to the characteristics of the process: fusion welding, pressure welding and brazing.
Welding through the following three ways to achieve the purpose of joining:
1, fusion welding – heating to join the workpiece to make the local melting to form a molten pool, the molten pool after cooling and solidification will be joined, if necessary, can be added to the fusion filler to assist, it is suitable for a variety of metals and alloys of welding process, no pressure.
2, pressure welding – welding process must apply pressure to the weldment, belonging to a variety of metal materials and part of the metal material processing.
3、Brazing-Adopting metal materials with lower melting point than the base material as brazing material, using liquid brazing material to wet the base material, fill the gap of the joints, and diffuse with the base material each other to realize the link weldment. Suitable for a variety of materials for welding processing, but also suitable for different metals or dissimilar materials welding processing.
In industrial production, fusion welding is the most widely used welding method, generally welded parts must go through the process of heating – melting – metallurgical reaction – solidification and crystallization – solid phase transition – the formation of joints and so on.
1.3 What is laser welding
Laser welding is a method of welding with heat generated by bombarding the weldment with a focused laser beam as an energy source. Due to the optical properties of laser refraction and focusing, laser welding is very suitable for welding of micro parts and parts with poor accessibility. Laser welding is also characterized by low heat input, small welding distortion, and is not affected by electromagnetic fields.
Laser welding is one of the important aspects of the application of laser material processing technology. 1970s is mainly used for welding thin-walled materials and low-speed welding, the welding process is heat conduction type, that is, the laser radiation heating the surface of the workpiece, the surface heat through heat conduction to the internal diffusion, through the control of the width of the laser pulse, energy, peak power and repetition frequency and other parameters, so that the workpiece melting, the formation of a specific molten pool. Due to its unique advantages, it has been successfully applied in precision welding of micro and small parts.
1.4 Laser welding classification
1.4.1 According to the control mode can be divided: manual laser welding machine, automatic laser welding machine, galvanometer laser welding machine
1.4.2 According to the laser can be divided: YAG laser welding machine, semiconductor laser welding machine, fiber laser welding.
1.4.3 laser welding according to the welding laser output power size is divided into: low power (≤ 1KW), medium power (1.5 ~ 10KW), high power (> 10KW) three categories.
1.4.4 According to the working mode of the laser, there are two types of laser welding: pulsed laser welding and continuous laser welding, in which the pulsed laser welding forms a round welding spot and overlaps each other to form a seam, and the continuous laser welding forms a continuous seam during the welding process.
1.4.5 Laser welding is categorized according to its mode of light output: ① continuous laser welding ② pulsed laser welding. Continuous laser welding forms a continuous weld seam during the welding process, while pulsed laser welding forms a circular weld joint and overlaps each other to form a seam (fish scale) during the welding process.
1.4.6 Laser welding is divided into modes: laser heat conduction welding and laser deep melting welding, the former laser power density used is low (105 ~ 106W/cm2), the workpiece absorbs the laser, only to reach the surface melting, and then rely on heat conduction to the workpiece to the internal transfer of heat to the formation of a molten pool. This welding mode of shallow depth of melting, depth and width is relatively small. The latter laser power density is high (106 ~ 107W/cm2), the workpiece absorbs the laser rapidly melted and even gasification, molten metal under vapor pressure to form small holes laser beam can be directly under the action of the hole bottom, so that the small holes continue to extend until the small holes in the vapor pressure and the surface tension of the liquid metal and gravity until the balance. Small holes with the laser beam moving along the welding direction, small holes in front of the melted metal flow around the small holes to the rear, solidified to form a weld. This welding mode has a large depth of fusion and a large depth-to-width ratio. In the field of mechanical engineering, deep-melt welding should generally be selected except for those micro-thin parts.
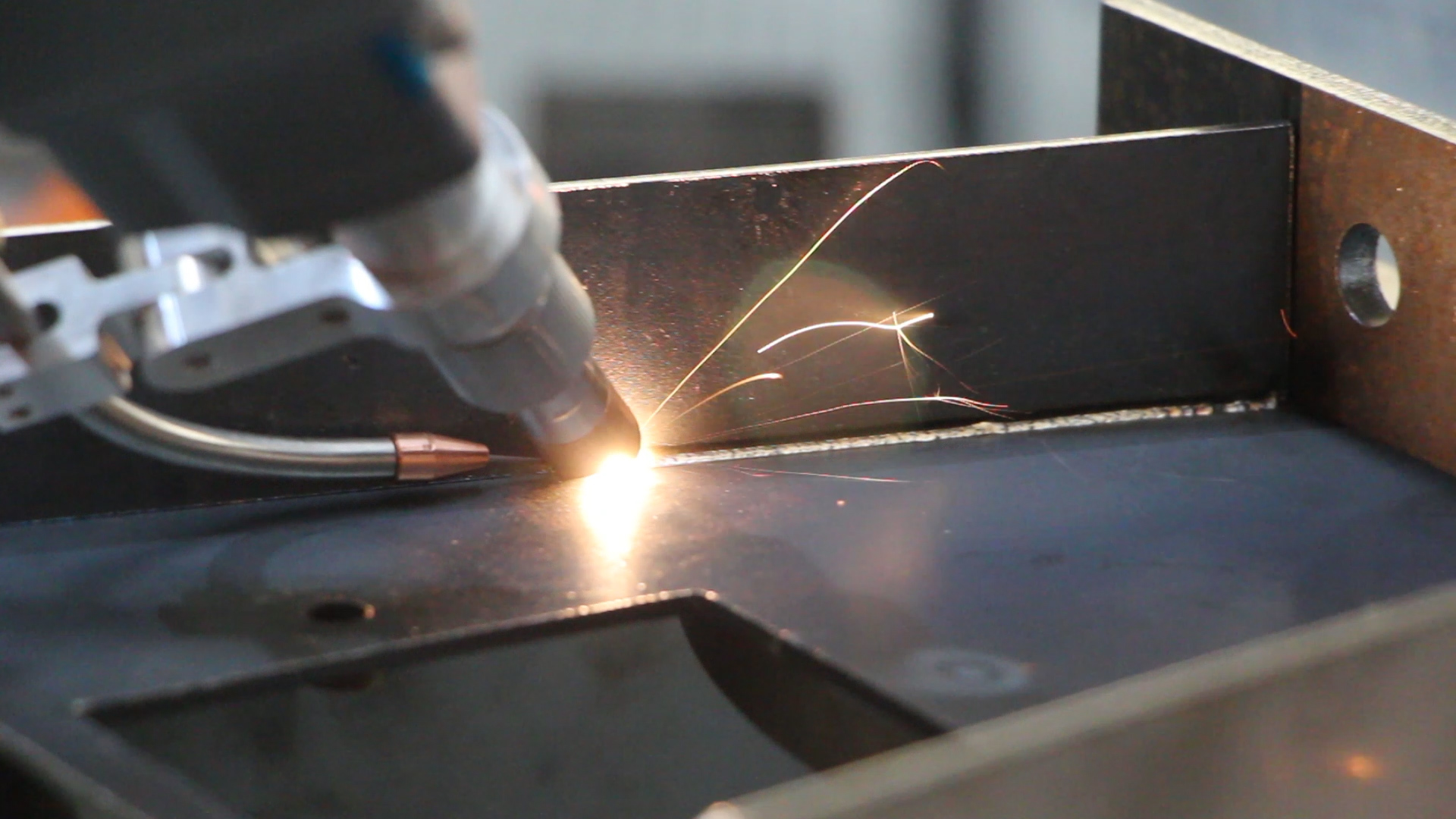

1.5 Modern laser welding technology
1.5.1 Laser filler welding
Laser filler welding is developed on the basis of single laser welding, compared to single laser welding has obvious advantages:
① Significantly reduce the assembly requirements of the workpiece, because there is a wire to join the welding process, the weld pool metal will be greatly increased to bridge a larger weld gap, and at the same time to make the weld seam is more full;
② control of the weld region of the organization of the properties of the weld because of the wire composition compared to the parent material composition of the weld joints have a certain difference. ② can control the organizational properties of the weld area, because the composition of the wire compared to the composition of the base material of the weld joint has a certain difference, the wire melted into the molten pool can be adjusted to the quality of the weld molten pool, composition and its ratio, to control the solidification process and the generation of microstructures;
③ line energy input is small, the heat-affected zone and the thermal deformation is small, very conducive to the welding of the deformation of the strict requirements of the workpiece;
④ can be realized in a small laser power welding of thicker materials, because the wire to join the welding process, can achieve multi-channel welding, and the weld can be made more full. Can realize multi-channel welding, and the weld pool metal will increase significantly, so that the weld joints can be broken open processing, as a way to reduce the actual laser welding thickness of the weldment, and then realize the multi-channel laser filler wire welding thick plate materials.
1.5.2 Laser Arc Composite Welding
combines the advantages of the two independent heat sources of laser and arc (such as laser heat source with high energy density, excellent directivity, and the characteristics of the transparent medium conduction, the arc plasma has a high thermal – electrical conversion efficiency, low equipment costs, operating costs, mature technology development, etc.), and greatly avoids the shortcomings of both (such as the high reflectivity of the metal material to the laser laser loss of laser energy, high equipment costs, low electrical – optical conversion efficiency, etc., while the two organic Reflectivity of the metal material to the laser caused by the loss of laser energy, laser equipment, high equipment costs, low electrical – optical conversion efficiency, etc., the lower energy density of the arc heat source, high-speed movement of the discharge stability is poor, etc.), at the same time, the organic combination of the two derived from a lot of new features (high energy density, high energy utilization, high arc stability, low tooling preparation accuracy and surface quality of the workpiece to be welded, etc.), so that it becomes a A new type of welding heat source with great application prospects.
1.5.3 Dual-beam laser welding
Dual-beam welding method is proposed, mainly used to solve the laser welding on the assembly accuracy of the adaptability and improve the stability of the welding process, improve the quality of the weld, especially for thin plate welding and aluminum alloy welding. Dual-beam laser welding, the same laser can be separated into two separate beams of light using optical methods to weld, but also can be combined using two different types of laser beams, CO2 laser, Nd: YAG laser and high-power semiconductor laser can be combined with each other. By changing the beam energy, beam spacing, and even the energy distribution pattern of the two beams of light, the welding temperature field is conveniently and flexibly adjusted to change the mode of existence of the hole and the flow of liquid metal in the molten pool, which provides a broader choice of welding process, which is incomparable to single-beam laser welding. It not only has the advantages of large melting depth, high speed and high precision of laser welding, but also has great adaptability for materials and joints that are difficult to weld by conventional laser welding.
1.5.4 Laser brazing
Laser welding is fusion welding, using a laser beam as an energy source and impacting on the weldment joint. Laser welding is non-contact welding, the process does not require pressure, but the need to use inert gas to prevent oxidation of the molten pool, filler metals are occasionally used. It does not need to be carried out in a vacuum, the disadvantage is that the penetration is not as strong as electron beam welding. Laser welding is capable of precise energy control, thus allowing the welding of precision micro devices. And it can be applied to many metals, especially to solve some difficult to weld metal and dissimilar metal welding.
Difference between laser fillet welding and laser fillet brazing
The form of laser fillet welding is shown in Figure 1, which is different from laser fillet brazing shown in Figure 2. The basic elements of the two welding methods are the same, are composed of a laser beam, wire, workpiece to be welded, the protective gas according to the actual need to decide whether to add, the main equipment involved in the wire feeder, welder, filler brazing soft gun head, welding head, high-power laser.
Although the two welding methods are basically no difference in the external form, but in essence there is a significant difference. Laser filler wire welding, the laser is generally selected high-power fiber laser, the laser not only need wire, but also need to melt the base material and the formation of laser deep-melt welding on the base material unique small hole effect, the formation of a deeper molten pool, the wire component and the base material metal components fully mixed to form a new mixed molten pool, the mixed molten pool of the elemental composition of the composition and its proportion, quality relative to the wire and the base material has a greater difference, so you can For the performance defects of the base metal itself, select the appropriate wire to add to the welding process, so that at the microscopic level of the weld crack resistance, fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance and other aspects of the purposeful improvement. In addition to this, laser fillet brazing can be used for multi-pass stack welding, as it can realize deep fusion welding with small hole effect, which can realize full fusion of the upper and lower passes to avoid serious defects of unfused passes, so as to have the ability to weld joints of large thicknesses.
Laser filler brazing, the laser is generally used for high-power semiconductor laser, the laser is almost entirely on the wire, only a very small amount of laser light will act on the weld and melt a small amount of the weld surface metal, and its melting pool is almost formed by the melted wire, so the performance of the weld is mainly dependent on the elemental composition of the wire and its proportion and the melted wire in the weld at the spread and the weld with the base metal of the weld combination, the main purpose of the weld is to achieve deep fusion of small holes. The main purpose of laser filler brazing is to achieve a certain connection strength and sealing of the welded joint, and, laser filler brazing can not be multi-stack welding, the upper and lower layers of the weld channel basically can not achieve full and effective fusion, joint mechanical properties are very poor.
1.5.5 Laser spot welding
Laser spot welding machine is mainly composed of laser, power supply and control, cooler, light guide and focusing, binocular body microscopic observation of several parts, compact structure, small size. With the laser beam coaxial micro-coordinate instructions, making it easy to locate the workpiece, without the need for special fixtures. Laser power, pulse frequency and pulse width can be preset and changed through the control panel. The power supply adopts a drawer-type structure and is easy to be removed, thus the equipment is easy to operate and maintain. There is no need to filler solder, high welding speed, reliable joints, small deformation of the workpiece and beautiful molding.