In recent years, the role of the laser cutting machine on the development of the sheet metal industry has become increasingly prominent. In the cutting process, there are six practical functions, with these practical functions, can greatly improve the laser cutting machine processing efficiency and cutting performance.

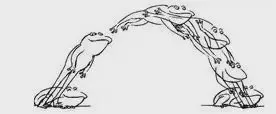
I. Frog Hopping
Frog jumping is the air travel method of the laser cutting machine. As shown in the figure below, after cutting hole 1 and then hole 2, the cutting head has to move from point A to point B. Of course, the laser has to be turned off during the movement. From point A to point B between the movement process, the machine “empty” running, called air travel.
The air travel of an early laser cutting machine is shown in the figure below, with the cutting head completing three actions in sequence: rising (to a sufficiently safe height), leveling off (to the top of point B), and descending.

Compressing the idle time improves the efficiency of the machine. If the three actions to be completed in sequence, to “at the same time” to complete, you can shorten the idle time: cutting head from point A to move towards point B, that is, at the same time up; close to the point B, at the same time down. As shown in the figure below.
2. automatic focusing
Cutting different materials requires that the focal point of the laser beam falls at different locations in the cross-section of the workpiece. Therefore, it is necessary to adjust the position of the focus (focusing). Early laser cutting machine, generally using manual focus; nowadays, many manufacturers of machines have realized the automatic focus.
Some people may say that it is good to change the height of the cutting head, the cutting head is raised, the focus position is high, the cutting head is lowered, the focus position is low. It’s not that simple.
In fact, in the cutting process, the distance between the nozzle and the workpiece (nozzle height) is about 0.5 to 1.5mm, which may be regarded as a fixed value, i.e., the height of the nozzle is unchanged, so you can’t adjust the focus by raising and lowering the cutting head (otherwise you can’t complete the cutting process).
The focal length of the focusing lens is unchangeable, so you can’t expect to adjust the focus by changing the focal length either. The focus position can be changed if the position of the focusing mirror is changed: if the focusing mirror is lowered, the focus is lowered, and if the focusing mirror is raised, the focus is raised. –This is indeed one way of focusing. Autofocus can be realized by using a motor to drive the focusing mirror in an up and down motion.
Another method of automatic focusing is: in the beam into the focusing mirror before the placement of a variable curvature mirror (or adjustable mirror), by changing the curvature of the mirror, change the angle of dispersion of the reflected beam, thereby changing the focus position. As shown in the figure below.
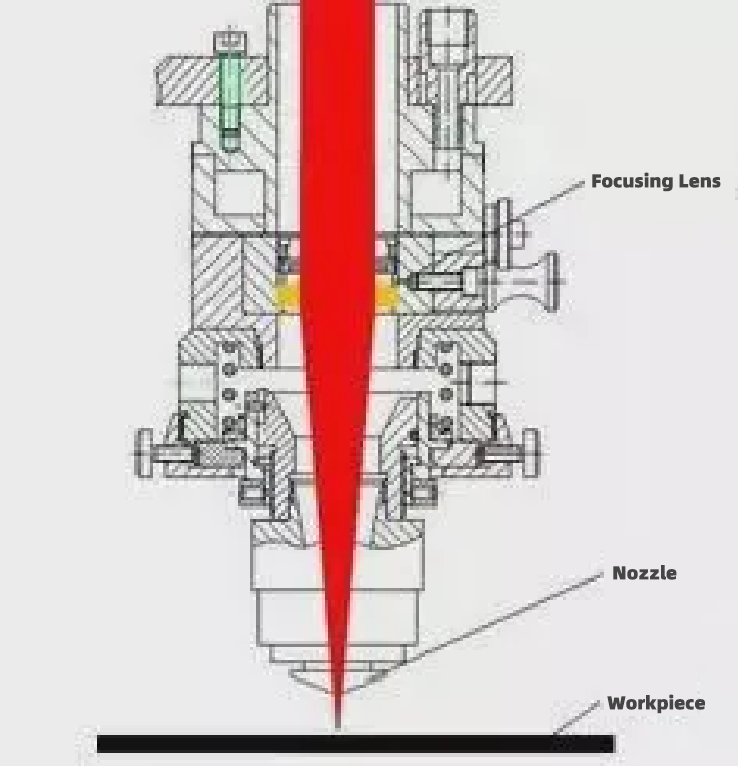
With the auto focus function, the processing efficiency of the laser cutting machine can be significantly improved: the piercing time of the thick plate is greatly reduced; processing of different materials and thickness of the workpiece, the machine can automatically adjust the focus to the most suitable position quickly.
3. automatic edge seeking
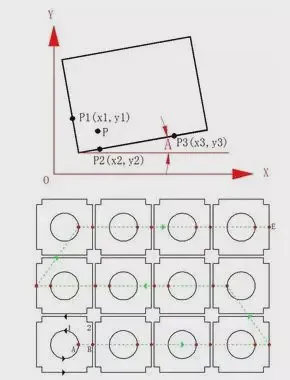
As shown in the figure below, when the sheet is placed on the table, if it is skewed, it may be wasted when cutting. If the tilt angle and origin of the sheet can be sensed, the cutting process program can be adjusted to fit the angle and position of the sheet to avoid waste. The automatic edge-seeking function was created.
When the automatic edge search function is activated, the cutting head starts from point P and automatically measures three points on the two vertical edges of the sheet: P1, P2, and P3, and automatically calculates the tilt angle A of the sheet and the origin of the sheet accordingly.
With the automatic edge finding function, the time spent earlier on adjusting the workpiece – which is not easy to do with workpieces weighing hundreds of kilograms on the cutting table – is saved, and the efficiency of the machine is increased.
A technologically advanced and powerful high-power laser cutting machine is a complex system of optical, mechanical and electrical integration. Subtleties, often hidden wonders. Let’s take a peek at its wonders.
4. Centralized piercing
Centralized perforation, also known as pre-piercing, is a process of processing, not a function of the machine itself. When laser cutting thicker plates, each contour of the cutting process has to go through two stages: 1. perforation, 2. cutting.
The conventional machining process (perforation at point A → cutting profile 1 → perforation at point B → cutting profile 2 → ……), the so-called centralized perforation, means that all the perforation processes on the whole board are executed centrally in advance, and then turn back to execute the cutting process.

With the centralized piercing process (complete piercing of all contours → return to the starting point → cut all contours), the total length of the machine’s trajectory is increased when centralized piercing is used compared to the conventional process. Then why is centralized piercing used?
Centralized piercing avoids overburning. During piercing of thick plates, heat builds up around the piercing point, and if cutting is done immediately afterward, overburning occurs. With the centralized piercing process, when all the perforations are completed and returned to the starting point for cutting, there is sufficient time to dissipate the heat, thus avoiding the phenomenon of over-burning.

Focused piercing can improve processing efficiency. At present, there are still many laser cutting machines that do not have the function of automatic focusing. For processing thick plates, the process parameters (laser mode, power, nozzle height, auxiliary gas pressure, etc.) are different for the piercing and cutting stages. The nozzle height is higher in the piercing process than in the cutting process. If the conventional processing process is adopted (contour 1 piercing → contour 1 cutting → contour 2 piercing → contour 2 cutting → ……), in order to ensure the quality and efficiency of cutting, the focus of the laser beam can only be manually adjusted to the optimal position according to the needs of the cutting (Imagine if it is like this: at the very beginning, the focus is adjusted artificially to the position required for piercing and Perforation; then, the focus will be adjusted to the position required for cutting, cutting; and then adjusted to the perforation position, perforation; ……; until the processing is complete – this is a nightmare). As a result, the focus is necessarily not in the optimal position for piercing, and the piercing time is longer.
However, by adopting a centralized piercing method, the focus can be adjusted to a suitable position for piercing, and then after the piercing is completed, the machine can be paused and the focus position can be adjusted to the optimal position required for cutting; in this way, the piercing time can be shortened by more than half, which greatly improves the efficiency. Of course, if necessary, but also in the centralized piercing and cutting in the middle of the adjustment or change other process parameters (such as air + continuous wave can be used for piercing, while the use of oxygen for cutting, with enough time in the middle of the completion of the gas switch). We generally refer to the automatic zoom of the drive focusing mirror as the F-axis; if we use manual zoom for centralized piercing and cutting like this, can we call it the “H” (Hand) axis “zoom”?
Centralized piercing also has risks. If a collision occurs during the cutting process, causing the sheet to shift position, the uncut portion may be scrapped. The centralized piercing process requires the help of an automatic programming system.
5. Bridge position (micro-connection)
When performing a laser cutting process, the sheet is held up by serrated support strips. Parts that are cut down, if not small enough to fall through the gap in the support bars; and if not large enough to be held up by the support bars; may lose balance and buckle. The cutting head moving at high speed may collide with it, resulting in a minor shutdown or damage to the cutting head.
Utilizing the bridge position (micro-connection) cutting process, this phenomenon can be avoided. In the laser cutting of graphics programming, intentionally closed contours, disconnect a number of places, so that after the completion of the cut parts and the surrounding material to stick together, not to fall, these disconnections, is the bridge position. Also known as breakpoints, or micro-connections (this call stems from a raw translation of MicroJoint). The distance of the break, about 0.2 to 1mm, is inversely proportional to the thickness of the sheet. Based on different perspectives, there are these different calls: based on the contour, disconnected, so called breakpoint; based on the part, adhered to the base material, so called bridge position or micro-joint.
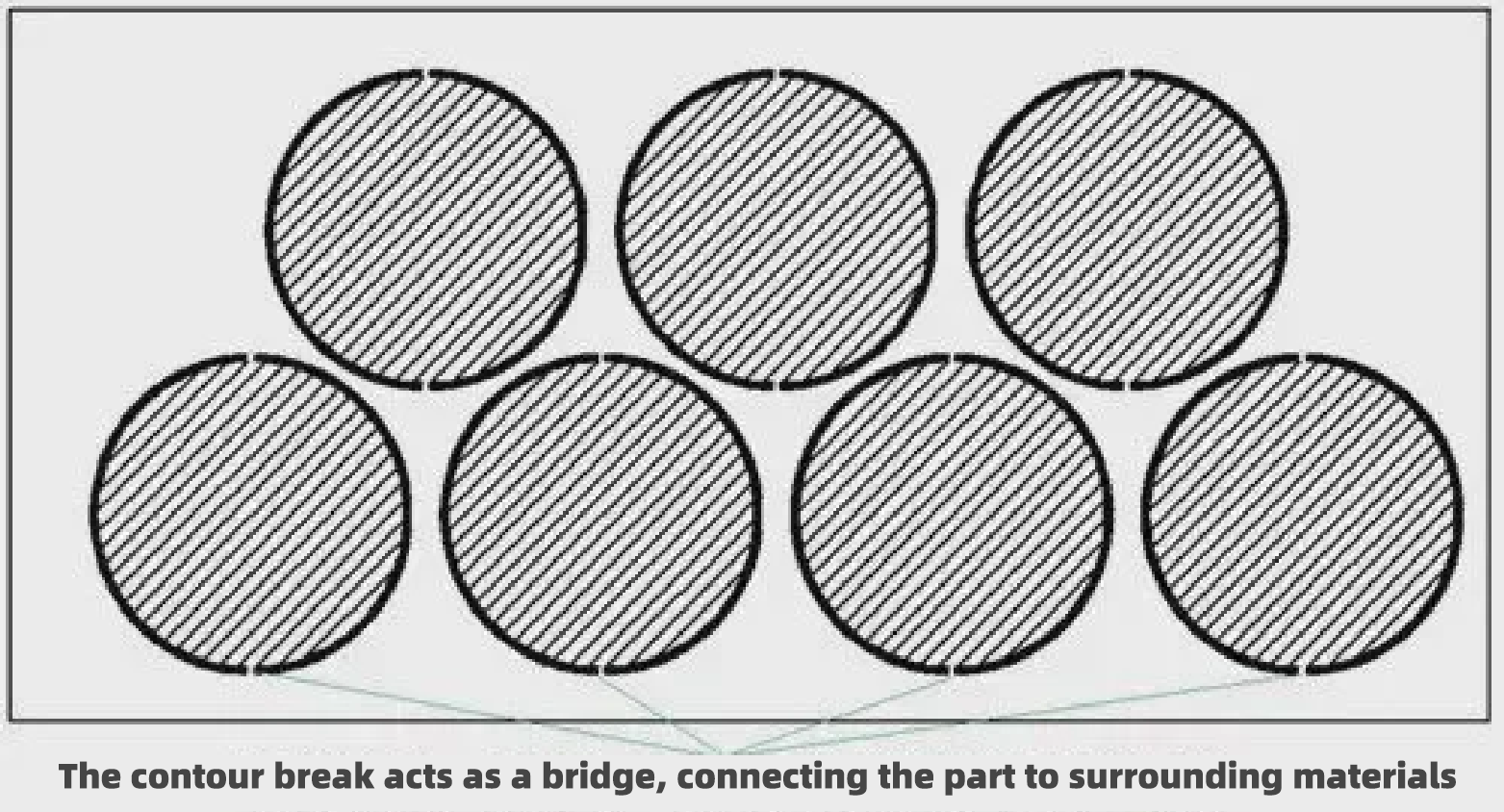
Bridge bits connect the part to the surrounding material. Sophisticated programming software automatically adds the right number of bridge bits according to the length of the contour. It also distinguishes between inner and outer contours and decides whether to add bridge bits, so that the inner contour (scrap) without bridge bits falls off, while the outer contour (part) with bridge bits sticks to the base material and doesn’t fall off, thus eliminating the need for sorting.
6. Common edge cutting
If the contour of neighboring parts is straight, and the same angle, it can be combined into a straight line, only cut once. This is a common cutting. Obviously, common cutting reduces the cutting length, can significantly improve processing efficiency.
Common Cutting does not require that the shape of the part be rectangular. This is illustrated in the figure below.
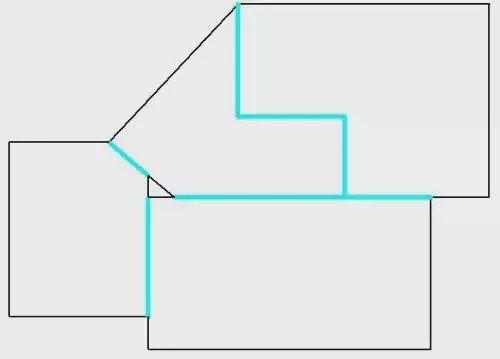
The azure line is the common edge, common edge cutting, not only saves the time of cutting, but also reduces the number of perforations, so the benefits are very obvious. If you save 1.5 hours per day due to common edge cutting, about 500 hours per year, the cost per hour of the integrated cost of $ 100, it is equivalent to an additional $ 50,000 a year to create benefits. Common edge cutting needs to rely on intelligent automatic programming software.