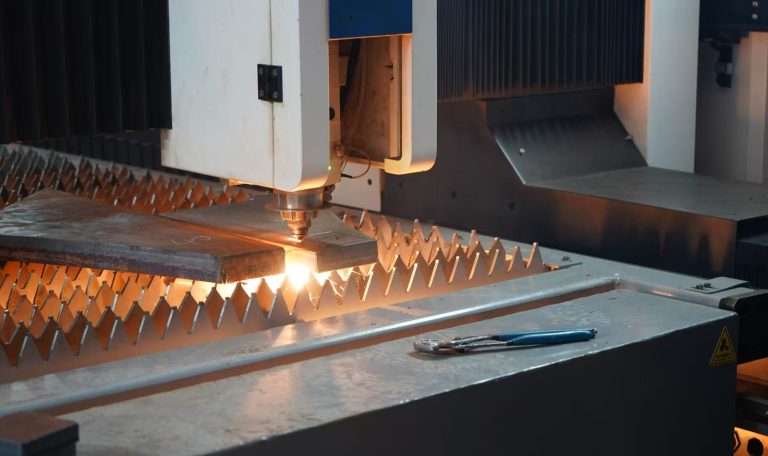
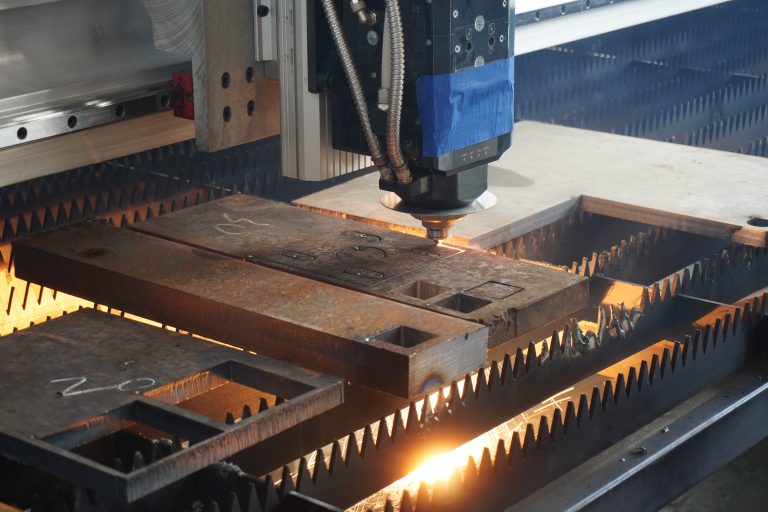
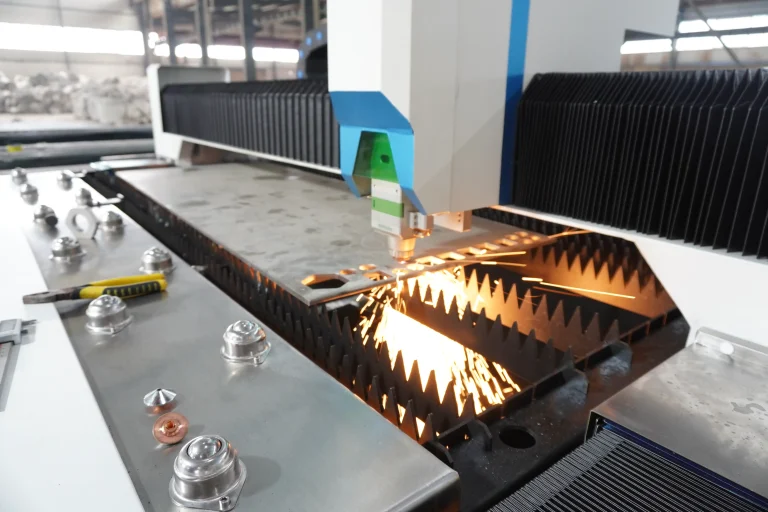
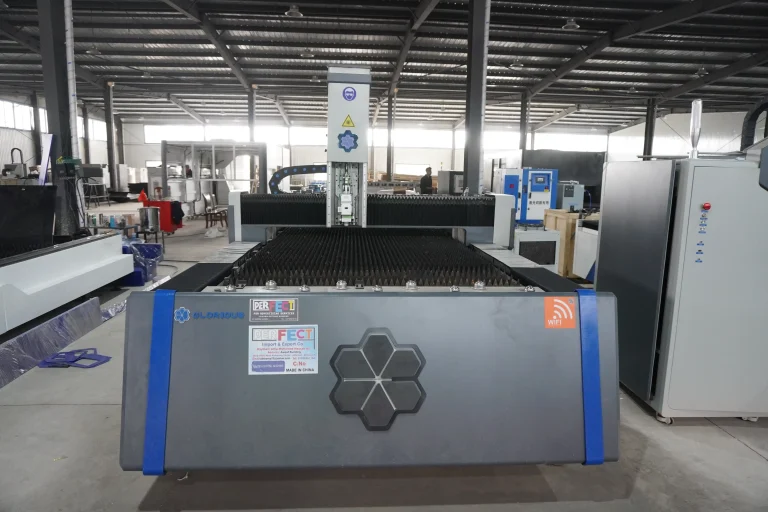
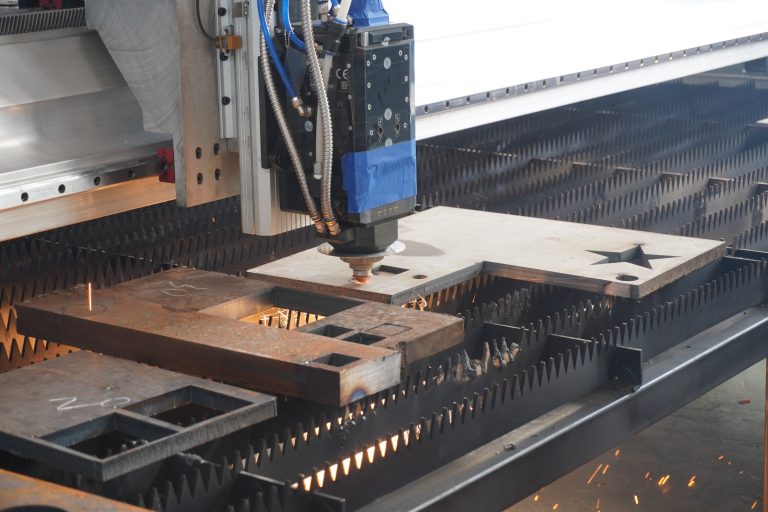
As modern manufacturing rapidly evolves toward greater speed and precision, higher demands are placed on processing technologies, particularly bevel cutting techniques. To meet the needs of transformation and upgrading, Ganghang Installation has introduced a versatile “power tool”—the laser flat-bed bevel cutting machine. Simultaneously, to accommodate diverse production requirements, the company retains flame cutting and plasma cutting capabilities, comprehensively enhancing production efficiency and product quality.

Differences Between Flame Cutting, Plasma Cutting, and Laser Cutting
| No. | Item | Flame Cutting | Plasma Cutting | Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cutting Surface | Piercing, cutting | Piercing, cutting | Piercing, cutting, beveling |
| 2 | Cutting Thickness | Maximum thickness up to 350 mm; suitable for large-scale cutting of common steel plates | Optimal cutting thickness: 20 mm; suitable for medium-thickness materials | Batch cutting: carbon steel: 1–80 mm, non-batch: up to 90 mm Stainless steel: batch: 1–65 mm, non-batch: up to 100 mm |
| 3 | Materials Suitable | Common steel plates | Suitable for various metals including stainless steel, aluminum plates, etc. | Wider application range: cuts both metals and non-metals (including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloys, galvanized steel, titanium alloys, copper, etc.) |
| 4 | Cutting Speed & Quality | Slow speed, good precision, vertical cut surface | Fast speed, lower precision, slightly inclined cut surface | Fastest speed (maximum cutting speed: up to 10 m/min) Very narrow kerf, cut edges parallel and perpendicular to the surface, dimensional accuracy: 0.1–0.3 mm Low noise, no pollution, easier to achieve automated cutting. Although initial investment is higher (laser), long-term machining cost is at least 50% lower than traditional methods |
| 5 | Energy Consumption & Smoke | Lowest energy consumption, minimal smoke | High energy consumption, high smoke volume; requires powerful dust extraction equipment | Moderate energy use, low smoke emission, excellent smoke removal effect |
| 6 | Cutting Process | Piercing, cutting | Piercing, cutting | One-machine integration (features wide application scope, flexible processing, high precision, good quality, clean production process, and ease of automation, flexibility, intelligence, etc.) |
Laser flat bevel cutting utilizes the energy released when a laser beam strikes the workpiece surface to melt and vaporize the material, achieving the cutting objective. This method is not constrained by cutting patterns, offering features such as automatic layout for material savings, smooth cut edges, and low processing costs.
Feature Overview
- Multi-Functional Machine
High-performance cutting production equipment that handles multiple requirements—including plate cutting and beveling—with a single machine.
- Larger Processing Dimensions
Maximum cutting dimensions for flat plate straight cutting: 3500 × 26000 mm
Maximum cutting dimensions for flat plate beveling: 3200 × 25000 mm
Cutting thickness range: 1–80 mm
Product Features
- One-Step Forming
Seamlessly integrated with Tekla 3D modeling software, it completes all feature cutting in a single operation—including cutting, circular holes, notches, bevels, and marking. This transforms traditional multi-step processes into one-step forming, streamlining production and reducing manufacturing and labor costs.
- High Efficiency
The high-performance sheet-following control system drives the 3D cutting host at a maximum speed of 40m/min. Its dynamic performance boosts productivity, efficiently handling large-format sheet cutting.
- High Precision and Quality
The laser beam’s focused spot achieves millimeter-level accuracy or finer, enabling precise execution of complex cuts. Results are clean and smooth, minimizing post-processing requirements.
- Non-Stop Production
Features a dual-station design for uninterrupted loading and unloading, enabling high-speed, efficient production that doubles output capacity.
The choice of cutting technology depends on specific application requirements and material properties. Oxy-fuel cutting is suitable for large-scale, low-cost cutting needs; plasma cutting is ideal for rapid cutting of medium-thickness metals; laser cutting excels in high-precision, demanding cutting tasks, particularly in the processing of both metallic and non-metallic materials.