Laser cutting is widely used in carbon steel processing due to its high precision and efficiency. However, common issues such as dross (burrs), incomplete cutting, and abnormal sparks can significantly affect cut quality and production efficiency. In this article, we explore the three most frequent problems encountered when laser cutting carbon steel and provide practical troubleshooting solutions to help manufacturers improve cut accuracy and reduce downtime.
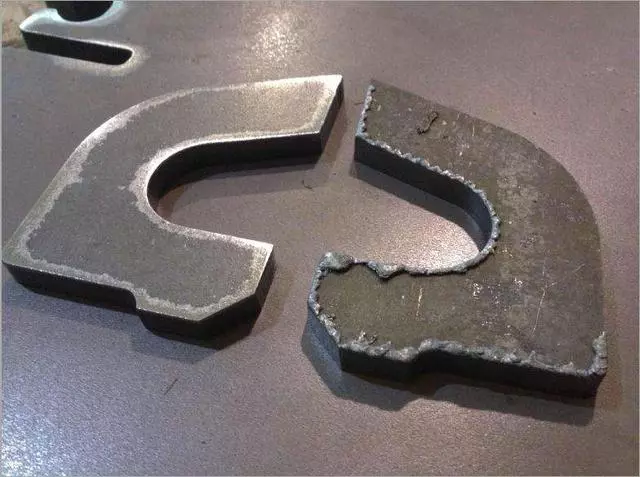

- Burrs on machined parts when laser cutting carbon steel
Generally cause burrs on processed parts, the possible reasons include:
(1) laser focus position offset, do focus position test, according to the laser focus offset amount to adjust;
(2) laser output power is not enough, you need to check whether the laser generator is working properly, if normal, then observe the laser control button output value is correct, if not correct to adjust;
(3) cutting line speed is too slow, need to increase the line speed in the operation control;
(4) cutting gas purity is not enough, need to provide high-quality cutting gas;
(5) machine running time is too long instability, this time you need to shut down and restart.
- Laser incomplete cutting
Reasons for incomplete laser cutting:
(1) laser nozzle selection and processing plate thickness mismatch, replace the nozzle or processing plate;
(2) laser cutting line speed is too fast, need to operate the control to reduce the line speed.
- Cutting mild steel appears abnormal sparks
Normal cutting mild steel, spark beam long, flat, less open fork. The emergence of abnormal sparks will affect the smoothness of the cut section of the processed parts and processing quality.
At this time in the case of other parameters are normal, the following should be considered:
(1) The laser head nozzle loss is serious, should be replaced in a timely manner nozzle;
(2) In the absence of a new nozzle replacement, the cutting gas pressure should be increased;
(3) If the nozzle and the laser head connection threads loose, then you should immediately pause the cutting, check the laser head connection status, re-apply the threads.
In conclusion, the three most common issues in laser cutting carbon steel—dross formation, incomplete cuts, and abnormal sparks—are often caused by laser focus deviation, incorrect process parameters, nozzle wear, or low-purity assist gas. By performing regular equipment maintenance, optimizing cutting settings, and using high-quality consumables, these problems can be effectively prevented. Understanding these root causes and solutions not only improves cut quality but also enhances machine uptime and reduces operational costs. Implementing standardized operating procedures ensures consistent, high-efficiency laser cutting in industrial applications.