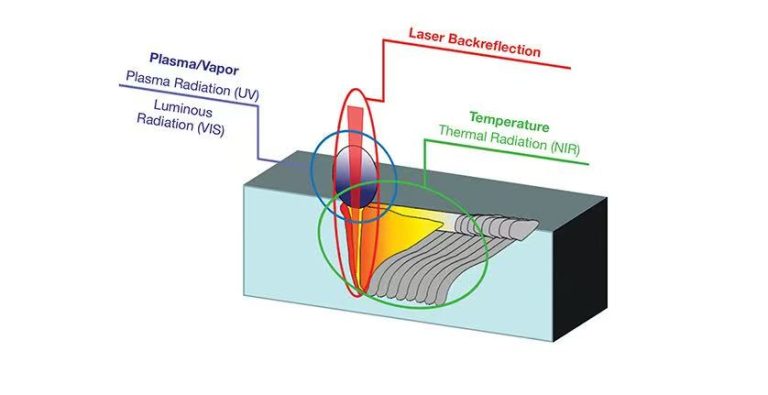
1.Laser welding technology
Laser welding is one of the most important aspects of the application of laser processing technology. Laser welding is the use of laser radiation energy to achieve effective welding process, its working principle is: through a specific way to stimulate the laser active medium (such as CO2 and other gases of the gas mixture, YAG Yttrium Aluminum Garnet crystals, etc.), so that it is oscillating back and forth in a resonant cavity, thus forming the stimulated beam of radiation, when the beam is in contact with the workpiece, the energy is absorbed by the workpiece, in the temperature reaches the melting point of the material will be When the temperature reaches the melting point of the material, welding can be carried out.
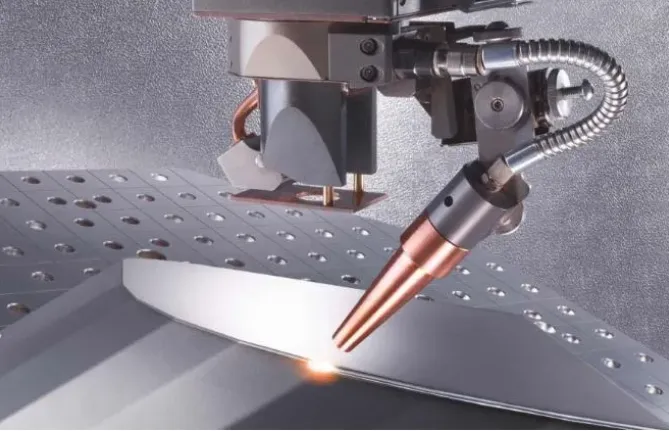

2.Important parameters for laser welding technology
①power density:
Power density is one of the most critical parameters in laser processing. The use of higher power density, in the microsecond time frame, the surface layer can be heated to the boiling point, producing a large number of vaporization. Therefore, high power density is favorable for material removal processes such as drilling, cutting, and engraving. For lower power density, the surface layer temperature to reach the boiling point needs to undergo a few milliseconds, before the surface layer of vaporization, the bottom layer to reach the melting point, easy to form a good melt welding.
②laser pulse waveform:
When the high-intensity laser beam to the surface of the material, the metal surface will have 60 to 98% of the laser energy reflection and loss, especially gold, silver, copper, aluminum, titanium and other materials reflective, fast heat transfer. A laser pulse signal process, the reflectivity of the metal with time and change. When the surface temperature of the material rises to the melting point, the reflectivity will drop rapidly, and when the surface is in the melting state, the reflection stabilizes at a certain value.
③Laser Pulse Width:
Pulse width is an important parameter of pulsed laser welding. Pulse width is determined by the depth of melting and heat-affected zone, the longer the pulse width, the larger the heat-affected zone, and the depth of melting increases with the 1/2 power of the pulse width. However, an increase in pulse width reduces the peak power, so increasing the pulse width is generally used for heat transfer welding methods, forming a wide and shallow weld size, especially suitable for lap welding of thin and thick plates.
However, lower peak power will lead to excess heat input, each material has an optimal pulse width to maximize the depth of fusion.
④the amount of out-of-focus:
laser welding usually need a certain amount of out-of-focus, because the laser focus at the center of the spot power density is too high, easy to evaporate into a hole. Away from the laser focus of the various planes, the power density distribution is relatively uniform.
⑤there are two types of defocusing:
positive defocusing and negative defocusing. Focal plane is located above the workpiece for positive defocus, and vice versa for negative defocus. According to the theory of geometric optics, when the positive and negative defocusing plane and welding plane at equal distances, the corresponding plane of power density is approximately the same, but in fact the shape of the molten pool obtained by a certain difference. Negative defocusing, you can get a greater depth of fusion, which is related to the formation process of the molten pool.
⑥welding speed:
welding speed has a greater impact on the depth of melting, increase the speed will make the depth of melting shallow, but the speed is too low will lead to excessive melting of the material, the workpiece weld through. Therefore, a certain laser power and a certain thickness of a particular material has a suitable range of welding speed, and in which the corresponding speed value can be obtained when the maximum depth of fusion.
⑦shielding gas:
laser welding process often use inert gas to protect the molten pool, for most applications often use helium, argon, nitrogen and other gases for protection. The second role of the protective gas is to protect the focusing lens from metal vapor contamination and liquid droplet sputtering, in high-power laser welding, the ejector is very strong, this time to protect the lens is more necessary. The third role of the protective gas is effective in dispersing the plasma shielding generated by high-power laser welding. The metal vapor absorbs the laser beam and ionizes into equal plasma, and if too much plasma is present, the laser beam will be consumed by the plasma to some extent.

3.Unique effects of laser welding technology
Compared with traditional welding technology, it has four unique effects:
①weld purification effect
When the laser beam irradiated to the weld, due to the material in the oxide and other impurities in the laser absorption rate than the metal to the laser absorption rate is much higher, therefore, the weld in the oxide and other impurities are rapidly heated and vaporized to escape, so that the weld in the impurity content is greatly reduced. Therefore, laser welding not only does not pollute the workpiece, but can play a purifying role in the material.
②light burst impact effect
When the laser power density is very high, under the irradiation of a powerful laser beam, the weld metal in the rapid evaporation gasification. Under the action of high-pressure metal vapor, the molten metal in the molten pool produces explosive splash, and its powerful shock wave to the depth of the hole direction propagation, the formation of elongated deep holes. In the laser constantly moving welding process, the surrounding molten metal continuously fill the cavity, condensed into a solid deep melt welding seam.
③deep melting welding of small hole effect
In the power density of up to 107W/cm2 of the laser beam irradiation, its energy input weld rate is much greater than the rate of heat conduction, convection, radiation dissipation, so that the laser irradiation area of the metal quickly vaporized, under the action of high-pressure steam, in the molten pool to form small holes. This hole is like a black hole in astronomy, can absorb all the light energy, the laser beam through this hole directly to the bottom of the hole, the depth of the hole determines the depth of melting.
④the melt pool in the hole side walls of the laser focusing effect
In the process of forming holes in the molten pool under laser irradiation, due to the incident angle of the laser beam incident to the side wall of the hole is usually larger, so that the incident laser beam in the hole side wall reflection and transmission to the bottom of the hole, thus appearing in the hole in the superposition of beam energy phenomenon, can effectively increase the intensity of the beam in the hole, a phenomenon known as the focusing effect of the side wall of the hole. This phenomenon is called the cavity sidewall focusing effect. The reason why lasers can be used for welding is based on the results of the above effects.
4.Advantages of laser welding technology
The unique effect of laser welding makes laser welding has the following advantages:
① the laser irradiation time is short, the welding process is extremely rapid, not only conducive to improving productivity, and the welded material is not easy to oxidize, the heat-affected zone is small, suitable for heat-sensitive transistor components welding. Laser welding neither slag, nor need to remove the oxidized film of the workpiece, and even through the glass for welding, especially suitable for micro-precision instrumentation in the welding.
②the laser can not only weld the same kind of metal materials, but also can weld heterogeneous metal materials, and can even weld metal and non-metallic materials. For example, with ceramics as a substrate for integrated circuits, due to the high melting point of ceramics, and should not be applied pressure, using other welding methods is very difficult, while the laser welding is more convenient. Of course, laser welding can not weld all the heterogeneous materials.
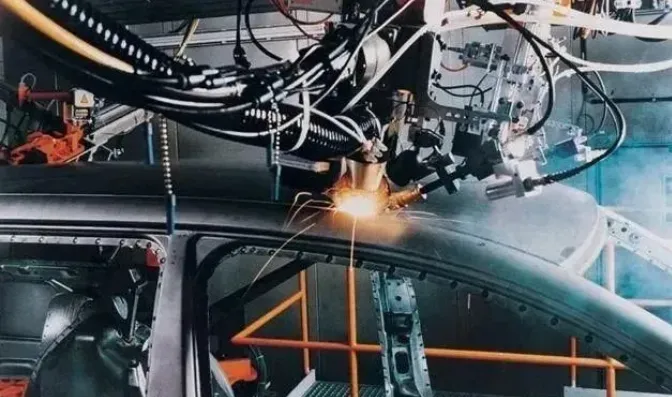
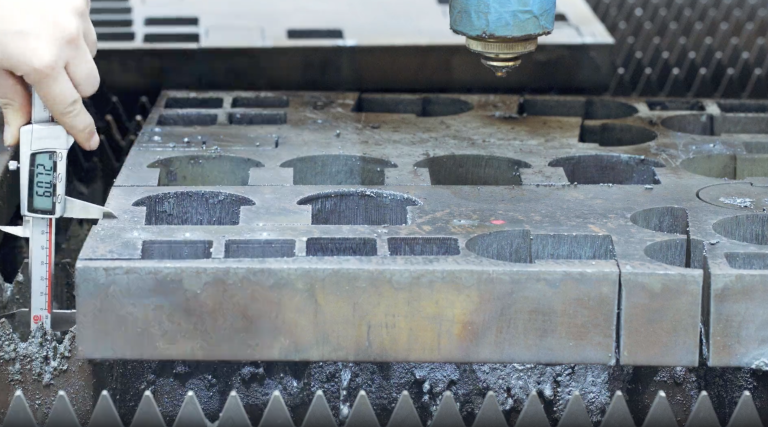
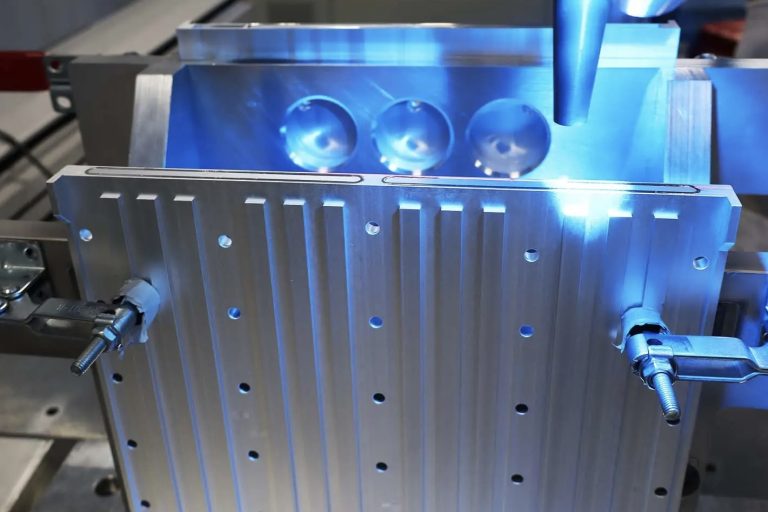
Applicable scenes and industries of laser welding: 1. Heat conduction welding is mainly used for precision processing, such as visible edge processing of thin metal sheets, medical technology, etc.; 2. Deep fusion welding and brazing are mainly used in the automotive industry, in which deep fusion welding is used for the body, transmission, shell, etc.; brazing is mainly used for body welding; 3. Laser conduction welding can deal with non-metals, and has a wide range of applicability, which can be used for consumer goods, automotive industry, Electronic housings, medical technology, etc.; 4. Composite welding is mainly used for special steel constructions, such as ship decks.